Economic Contribution of Smartphone Manufacturing in the UK
Smartphone manufacturing plays a significant role in the UK economy, contributing both directly and indirectly to national economic growth. This sector supports a variety of jobs, from assembly line workers to high-tech engineers, and fosters innovation that drives competitiveness globally.
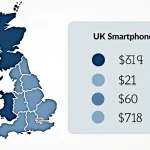
Measured by GDP contribution, UK smartphone manufacturing accounts for a notable percentage of the country’s manufacturing output. Recent data indicates that the sector generates billions in annual output, reinforcing its importance within the broader manufacturing landscape. The economic impact extends beyond production, influencing supply chains, distribution, and retail sales.
Also read : How are UK smartphones driving innovation in computing?
When compared to other UK manufacturing sectors, smartphone manufacturing exhibits dynamic growth and higher value-add per unit produced. For instance, while traditional automotive and aerospace industries remain substantial contributors to GDP, the smartphone manufacturing sector is recognized for its rapid innovation cycle and scalable production. This positions it as a key player in adapting the UK market to future technology demands.
Understanding this economic impact highlights the strategic importance of supporting UK smartphone manufacturing through policies that encourage investment, skills development, and innovation. Such measures ensure the sector continues to enhance its contribution to UK GDP and strengthens domestic industrial capabilities.
Have you seen this : How do UK smartphone prices compare to the rest of Europe?
Employment and Job Creation
Smartphone manufacturing in the UK significantly affects job creation across various sectors. Direct employment includes factory workers, engineers, and quality controllers in manufacturing facilities. These roles require a range of skills, from manual assembly to technical expertise, contributing to a diverse workforce impact.
Beyond the factory floor, substantial indirect jobs emerge in supply chains, logistics, and after-sales services. For example, companies providing components, packaging, and transport all rely on the manufacturing base, allowing for a ripple effect in employment. This network supports many ancillary roles that might not be immediately visible but are crucial for the overall industry health.
Regionally, the presence of smartphone manufacturing can revitalize local economies by attracting skilled workers and creating opportunities in related sectors such as IT services and retail. In areas traditionally dependent on manufacturing, these jobs help sustain communities and reduce economic disparities.
Overall, UK tech jobs associated with smartphone production are a mix of both traditional manufacturing employment and growth in technologically advanced roles. This blend enables a broad scope for career development and economic stability, driving forward the country’s position in the global tech industry.
Investment and Innovation in the Sector
Investment in UK technology has seen a significant uptick, drawing both domestic and international capital. This inflow fuels crucial R&D activities that drive economic growth. Companies and venture capitalists alike recognize the UK’s commitment to innovation, catalyzing further investment in cutting-edge research.
Research and development (R&D) remains a cornerstone of this ecosystem. Through focused R&D, the UK tech sector has achieved remarkable advancements, particularly in smartphone innovation. Improvements in processing power, battery technology, and software integration all stem from sustained capital flow supporting inventive projects.
International investment complements domestic efforts. Foreign investors often bring not just funds, but knowledge and market access, amplifying the impact of local R&D. This synergy enables the UK to compete globally, particularly in sectors influenced by smartphone production trends, such as miniaturization of components and wireless communication technologies.
Overall, the volume and diversity of investment ensure that the UK remains a hotbed for innovation. Continuously increasing capital flow allows ongoing breakthroughs, further enhancing the nation’s standing in smartphone technology and broader tech markets.
Supply Chain and Related Industries
The supply chain impact of evolving technology in UK electronics is profound, especially for component manufacturing. Local suppliers are increasingly required to meet higher standards of precision and innovation, driving improvements in production quality. This creates a competitive environment where UK-based component manufacturers invest in advanced techniques to stay relevant.
Moreover, advancements in electronics ripple through logistics and transportation services. Efficient supply chains depend on timely and reliable transport, prompting logistics firms to adopt digital tracking, automation, and optimized routing. These improvements reduce delays and costs, benefiting the entire industry.
The positive effects extend to related service sectors, including warehousing and distribution, which become more technologically capable. Such enhancements not only bolster the core electronics market but also generate spillover benefits for other tech and manufacturing sub-sectors. For example, automation in component handling aids automotive and aerospace supply chains, linking diverse industries in a shared ecosystem.
In summary, strengthening the supply chain in UK electronics advances component manufacturing and logistics, fostering a robust industrial network. This interconnected growth helps maintain the UK’s competitive edge in high-tech manufacturing on an international scale, while also opening avenues for innovation and efficiency improvements across multiple industries.
Export, Import, and Trade Balance
Understanding the trade balance is crucial when assessing the UK’s position in the global market, particularly in manufactured electronics. UK exports in this sector significantly contribute to the country’s export revenues, showcasing competitive products ranging from consumer electronics to specialized components. These exports help sustain jobs and drive innovation within the UK economy.
However, the UK’s import dependency remains high, particularly for parts and raw materials essential for electronic manufacturing. This reliance on imports can impact production costs and supply chain stability, making the industry vulnerable to global market fluctuations and trade disruptions.
When comparing trade balances with other electronics manufacturers internationally, the UK often experiences a trade deficit in this product category. This means imports exceed exports, which may reflect either strong domestic demand for foreign components or competitive international producers outpacing UK exports. Addressing this imbalance involves enhancing local manufacturing capabilities and investing in technologies that reduce the need for imported materials.
In summary, while UK exports in manufactured electronics contribute positively to the economy, the import dependency and resulting trade balance highlight areas needing strategic focus to improve the UK’s standing in the competitive global market.
Tax Revenue and Public Finances
Smartphone manufacturing significantly impacts tax revenue, contributing to government finances through multiple channels. Manufacturing facilities generate corporation tax from their profits, which directly supports national budgets. Besides this, these operations stimulate local economies, increasing VAT collections as employees and suppliers spend earned income on goods and services.
Business rates, a crucial component of local authorities’ income, are levied on manufacturing plants and facilities. This ensures that local governments receive funding necessary for public services, infrastructure maintenance, and community development. The presence of smartphone production units typically elevates business rates, contributing to the economic benefits experienced by local councils.
The combined effect of corporation tax, VAT, and business rates enhances overall government finances, enabling increased public spending on healthcare, education, and transport. This ripple effect strengthens socio-economic conditions beyond the manufacturing sites. As production scales up or new facilities open, tax revenue inflows rise correspondingly, creating sustainable funding channels for public initiatives.
Effectively, the smartphone manufacturing sector serves as a catalyst for robust economic benefits by fostering a reliable tax base. This interplay between production activities and tax contributions underscores the sector’s role in stabilizing and expanding government finances at both local and national levels.
Challenges and Future Outlook
The UK manufacturing sector faces several critical industry challenges that hinder growth. Intense global competition pushes companies to innovate constantly, while supply chain disruptions—exacerbated by recent international crises—cause delays and increased costs. These obstacles demand resilience and agile strategies for survival and expansion.
A significant influence on the sector is the Brexit impact, which has introduced new trade barriers and regulatory complexities. Restrictions on the free movement of goods and labor have challenged manufacturers’ operational efficiency. Policy changes aimed at adapting to post-Brexit realities continue to reshape the landscape, requiring businesses to evolve quickly.
Global market shifts further complicate the outlook. As demand patterns adjust, manufacturers must align with evolving trends such as sustainability and digitalisation to remain competitive. Projections suggest that despite these hurdles, the industry holds potential for considerable contribution to the UK economy if it embraces innovation and adapts policies effectively.
Future of UK manufacturing depends heavily on navigating these multifaceted challenges. Addressing competition, optimizing supply chains, and leveraging policy opportunities could foster sustainable growth. Keeping abreast of market trends and investing in technology will be key to unlocking the sector’s long-term impact and resilience on the economic stage.